What is Bio-engineering?
Bio-engineering technique is the use of living vegetation or vegetation parts, either alone or in conjunction with civil engineering structures and non living plant materials, to reduce shallow- seated instability and erosion on slopes.
Soil bio-engineering can be divided into threes categories:
Vegetative plantings
True Bio-engineering
Bio Technical Techniques (engineering)
Vegetative plantings
Vegetative plantings are conventional plantings of grasses & shrubs in order to prevent surface erosion.
- The living material is not used with structural meaning.
- The erosion prevention function is carry out only once the vegetation is established.
True Bio-engineering
Plants or part of plants (seeds, seedlings, cuttings, branches etc.) etc itself provide both the vegetative and structural components of the design.
- Brush layers, wattling, Bamboo fencing etc.
- Cutting or branch parts as initial and primary soil reinforcing and stabilizing material
- During the growing season develop roots and sprouts foliage. It becomes a major structural component which grows stronger with time
True Bio-engineering Examples
- Brush Layering
- Bamboo Fencing
Bio-technical Engineering
- Living materials (plants) are combined or integrated with non living or structural materials
- Vegetative and structural components work together in mutually reinforcing and complimentary roles.
- Live crib walls, vegetated gabions, vegetated stone pitching etc.
- Structural elements provide immediate resistance to sliding, erosion, and wash out
- As vegetation becomes established, roots invade and penetrate the slope, binding it together
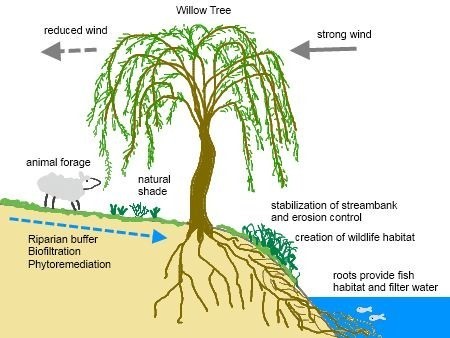
Engineering Function of Vegetation
- Catch
- Reinforcing
- Anchoring
- Armoring
- Supporting
- Drainage
Application of Bio Engineering
- Prevention of scour
- Protection of bare soil
- Stabilization of gullies, prevention of risk of gullying;
- All slopes where there is a risk of shallow slumps
- Any slope that remains bare; • any area that has failed and needs to be restored
- Rehabilitation of quarry sites and borrow pits
Scope / Field of Bio Engineering
- Mining and reclamation
- Highways and railways
- Construction sites
- Waste disposal and public health
- Airfields and helipads
- Waterways
- Land drainages
- Reservoirs and dams
- Coastal and shoreline protection
- Buildings and recreation
- Pipelines and site appraisal
Advantages of Bio Engineering
- Protect all slopes against erosion
- Low-cost and lower long-term maintenance cost
- Environmental benefits to wildlife habitat, water quality, and aesthetics
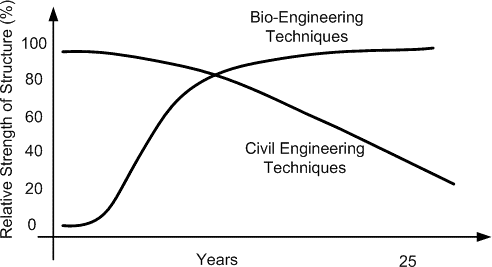
- Improved strength over time
- Improve surface drainage and reduce slumping
- Reduces shallow plane failure
- Compatible with environmentally sensitive sites
- Socially and economically advantageous to local communities
- Cost effective
Limitations of Bio Engineering
- Depth of root zone limits the performance of vegetation or bio engineering
- Not able to function in its initial stage
- Root penetration into foundations and drains
- Choking of waterways with plant growth
- Vegetation growth on structure cause adverse effect on the performance of structural material
- Needs aftercare, regular repair and maintenance.
Justification
- Less cost and less impact on slope
- Provide economic savings and minimize potential impacts to the slope and adjoining resources.
- Use of native plant materials and seed are well adapted to local climate and soil conditions.
- Useful on sensitive or steep sites where easy accessibility is not feasible.
- Grow stronger with time as vegetation becomes established.
- Even if plants die, organic litter helps growth of other plants.

Extremely useful information which you have shared here. This is a great way to enhance knowledge of galvanized planter box liners. for us, and also helpful for us. Thankful to you for sharing an article like this.
ReplyDeleteI read the above article and I got some knowledge from your article.Commercial concrete contractors. It's actually great and useful data for us. Thanks for share it.
ReplyDelete